Adrenaline
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a potent hormone and neurotransmitter produced by the adrenal glands. It is a key component in the body’s fight-or-flight response, which prepares the body to either confront or flee from a perceived threat. In a medical context, adrenaline can be administered as a medication to mimic this response in specific situations.
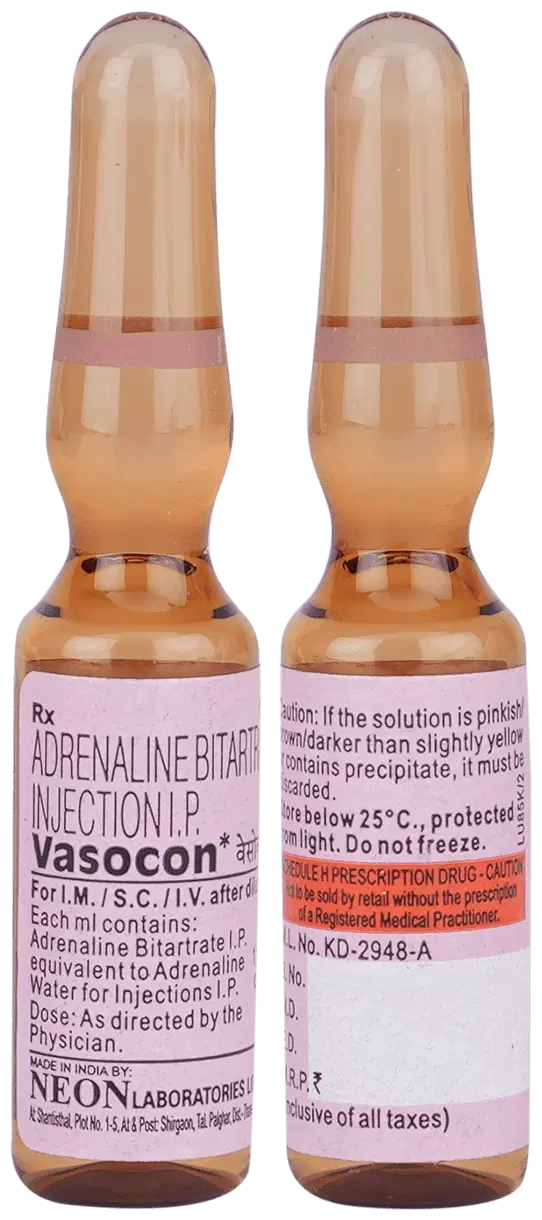
Adrenaline 1:1000 Injection is a combination medication that contains adrenaline and local anesthetics, such as lidocaine or prilocaine. This medication is used to numb a specific area of the body for procedures that require a high level of precision and minimal pain. Examples of such procedures include minor surgeries, removal of warts, or other skin lesions.
The 1:1000 ratio indicates that there is one milligram of adrenaline for every 1,000 milligrams of the local anesthetic. The adrenaline component works by constricting blood vessels, which helps to reduce bleeding and improve the effectiveness of the anesthetic. It also aids in reducing the absorption of the anesthetic into the bloodstream, allowing for a longer-lasting numbing effect.
Adrenaline should be used with caution and under the supervision of a healthcare professional, as it can cause serious side effects such as increased heart rate, high blood pressure, and even cardiac arrest if not administered properly. Patients with certain pre-existing conditions, such as heart disease or hypertension, may be at a higher risk of experiencing these side effects.
Showing all 10 results
Showing all 10 results


